Details of the POPCAT Market Manipulation
On November 13, an attacker orchestrated a liquidation attack on Hyperliquid's POPCAT market. This operation involved the use of $3 million in capital spread across 19 wallets, ultimately leading to a $4.9 million loss for HLP. The incident underscores vulnerabilities present in low-liquidity markets, impacting Hyperliquid's credibility and raising concerns about potential future risks within decentralized finance protocols.
Analyst @mlmabc revealed that the attacker utilized 19 distinct wallets and a capital investment of $3 million to execute the manipulation. The attacker established a substantial long position in POPCAT, estimated to be between $20 million and $30 million, employing 5x leverage. Subsequently, a massive buy wall was constructed and then abruptly removed, triggering a significant crash in the price of POPCAT.
This act of losing $3 million in a few seconds was not foolish or negligent, but a ‘deliberate attack’ against HLP and Hyperliquid.
Market reactions from within the industry were notably limited following the incident. Some community members voiced concerns regarding the potential for centralization risks during emergency response scenarios.
POPCAT market manipulation details
Historical Context and Future Safeguards
Historical precedents, such as the March 2025 JELLYJELLY incident, also involved illiquid token manipulations on Hyperliquid, which necessitated significant protocol interventions.
According to current data, Popcat trades at $0.13 with a market capitalization of $129.26 million and a 24-hour trading volume of $232.67 million, indicating a 400.73% increase. Despite recent volume spikes, the price experienced a 14.61% decrease in the last day, continuing a downward trend observed over the past 90 days.
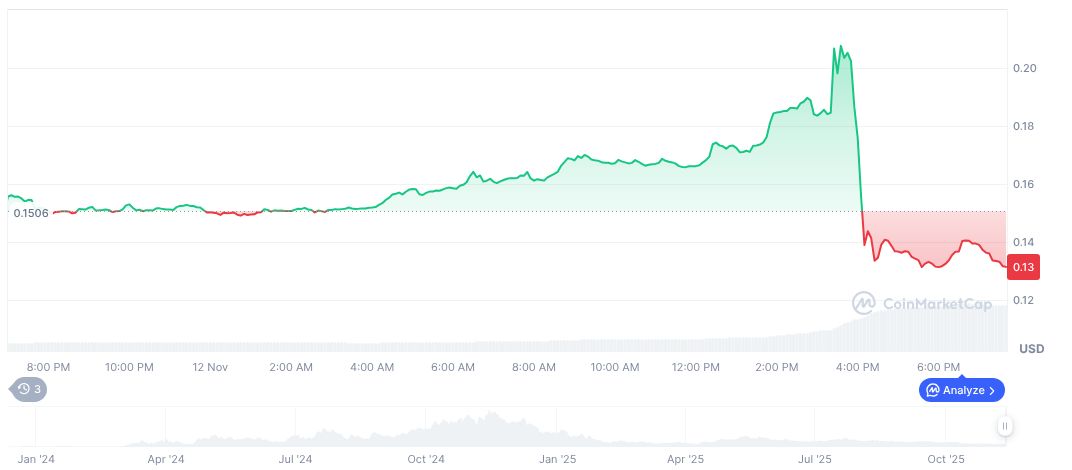
Experts suggest that this attack highlights the critical need for improved protocols to effectively handle market anomalies within decentralized exchanges. They advocate for the implementation of enhanced risk management tools and more robust liquidity provisions to mitigate the occurrence of similar events in the future. Strengthening algorithmic defenses and preventive governance measures remains paramount for ensuring long-term market stability.

