OpenAI has unveiled a new AI-powered web browser, ChatGPT Atlas, marking a significant move in its ambition to challenge Google Chrome's dominance in the market. The company announced the product during a livestream, positioning it as a browser built around the core capabilities of ChatGPT.
ChatGPT Atlas is initially launching worldwide on macOS, with versions for Windows, iOS, and Android planned for subsequent releases. OpenAI has stated that all users will have access to the browser upon its release, although a specialized "agent mode" will be exclusively available to Plus, Pro, and Business subscribers initially.
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman expressed the company's goal to fundamentally alter how humans interact with the internet. He suggested that "the chat experience in a web browser can be a great analog" for future internet usage. The new browser aims to seamlessly blend traditional web browsing with conversational AI, enabling users to navigate and engage with online content in a more natural, interactive way.

During the announcement, Altman was joined by OpenAI employees, including product lead Adam Fry and engineering lead Ben Goodger, who previously contributed to Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox. They elaborated on how Atlas integrates ChatGPT into the browsing experience.
ChatGPT Atlas Functions as a Personal Assistant
ChatGPT Atlas is designed to go beyond conventional web browsing, functioning as an intelligent assistant with contextual understanding that can act upon user prompts. A key feature is its memory capability, which allows the browser to retain user preferences, recent activities, and frequently visited pages, leading to a more personalized and efficient experience over time. Users can manage these "memories" in the settings or opt for private browsing using incognito mode.
The browser's agent mode represents another significant advancement. This mode empowers ChatGPT to execute simple tasks directly within the browser. Users can instruct it to book flights, make restaurant reservations, or edit documents, signifying OpenAI's progression towards making ChatGPT more proactive in completing tasks rather than just responding to queries.
This development builds upon earlier OpenAI projects like "Operator" and "ChatGPT Agent," which explored enabling the chatbot to perform actions on a computer. ChatGPT Atlas makes these capabilities more accessible by integrating them into a comprehensive browser environment for everyday users.
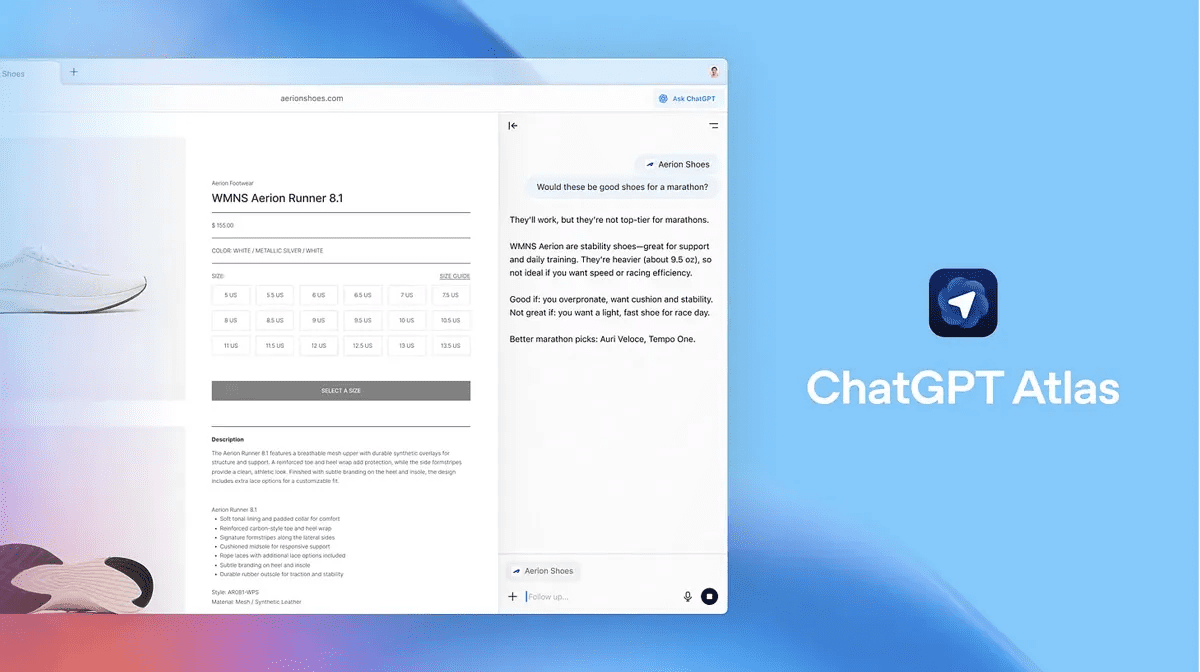
When a user clicks a link from a search result, Atlas displays a split-screen interface. One side shows the webpage as usual, while the other side features ChatGPT with a live transcription of a conversation. This provides users with an integrated assistant capable of summarizing, describing, or analyzing content in real-time, while maintaining full control over the displayed information.
A feature called "cursor chat" allows users to select text within an email or document and have ChatGPT rephrase it for clarity without needing to switch tabs or manually copy text. This streamlines editing processes.
Altman described ChatGPT Atlas as an "all-around great browser," praising its design and performance. However, the underlying objective appears to be a fundamental redefinition of a browser's role, shifting from mere page display to active content comprehension and interaction.
A New Phase in Browser Competition
The introduction of ChatGPT Atlas adds a new dimension to the competitive landscape often referred to as the "AI browser wars."
The past year has seen artificial intelligence companies focusing on browsers as a key area of innovation. OpenAI had previously signaled its interest with SearchGPT, an AI-powered search engine proof-of-concept. However, Atlas directly challenges Chrome by offering a full browsing experience, not just a search function.
OpenAI faces competition in this emerging market. AI firm Perplexity has launched its own AI browser, Comet, designed to simplify online search and task completion. Comet aims to provide direct answers and key links instead of presenting extensive search result pages, and it can also scan open tabs, summarize videos, and assist with online shopping.
Google is also enhancing Chrome by integrating its Gemini AI assistant more deeply. Google has indicated plans for Gemini to handle routine tasks such as grocery purchases and appointment scheduling, though specific release timelines have not been provided, and many of these features are still in development.

Microsoft has incorporated AI into its Edge browser through Copilot, but user experiences have been varied, with praise for ease of use alongside concerns about privacy and accuracy.
OpenAI's advantage in this increasingly competitive environment lies in the widespread familiarity and established user base of ChatGPT, which boasts tens of millions of monthly active users globally. By embedding ChatGPT at the core of its browser, OpenAI aims to offer users a familiar and trusted experience with enhanced accessibility and reduced friction.
What sets ChatGPT Atlas apart is its potential to fundamentally alter how people work and access information, beyond its aesthetic appeal.
Ultimately, OpenAI's success will hinge on user adoption. Google Chrome currently holds a dominant position in the browser market with over 3 billion users worldwide. Penetrating this established market will be challenging, particularly given Chrome's deep integration with Google's search and advertising ecosystems.

